Update PHP for a More Performant WordPress on Ubuntu 20.04
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
WordPress is one of the most popular free web publishing tools available. Authoring content on WordPress is straightforward, however, you need to perform regular maintenance on your WordPress site to keep it secure and up to date. One of those maintenance tasks is to regularly update PHP, which WordPress uses as a server-side programming language. This guide explains how and when to upgrade PHP without adversely affecting your site.
Why You Should Upgrade PHP for Applications Like WordPress
At regular intervals, a new version of the open-source PHP application is released. Older versions of the platform then, become obsolete. This means they are no longer updated and do not receive any further security patches. This allows vulnerabilities to accumulate and makes any site using an outdated version an easier target for intruders. Therefore, it is very important to use the minimum supported version of PHP and keep all PHP packages updated.
Some reasons to keep WordPress and PHP updated are listed below:
- An outdated PHP installation can cause security issues. These flaws might allow the site to be compromised.
- WordPress can have compatibility issues with older versions of PHP, especially after an update. Themes and plug-ins might not work with older versions.
- After PHP is updated, the site might run faster. Newer versions of PHP have performance improvements, and memory usage has also been improved.
- It often becomes more difficult to upgrade PHP if this task is left too long. Plug-ins and themes might not work properly afterward, which could require major rework.
Updating PHP is more complex than updating themes and plug-ins. PHP cannot be directly updated from the WordPress Dashboard. In addition, you should back up the site before upgrading PHP and, if necessary, restore it afterward.
Additional best practices for WordPress upgrades are listed below:
- Generate a routine or schedule for upgrades, including PHP upgrades.
- Update and upgrade the packages on the Linode regularly.
- Use strong passwords to access the WordPress Dashboard.
- Take regular backup copies of the site and its database.
- Regularly upgrade themes or plug-ins and keep all licenses.
Before You Begin
If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our Getting Started with Linode and Creating a Compute Instance guides.
Follow our Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access. Do not follow the Configure a Firewall section yet as this guide includes firewall rules specifically for an OpenVPN server.
A full LAMP stack must already be installed. See the How to Install a LAMP Stack on Ubuntu 20.04 guide for more details.
WordPress should already be installed. See the Linode guides on Installing WordPress and Deploying WordPress from Marketplace Apps.
sudo. If you are not familiar with the sudo command, see the
Linux Users and Groups guide.How to Update PHP
PHP usually has to be upgraded in one of two situations; when WordPress is first installed, or when it is upgraded to a newer version. Currently, the minimum recommended version of PHP is 7.4, while the latest version of PHP is 8.0. This guide describes how to update PHP to version 7.4. These instructions are designed for Ubuntu users but are generally applicable to all Linux distributions.
How to Determine if PHP Should Be Updated
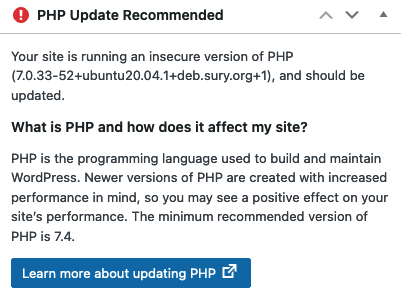
The easiest way to tell whether the current version of PHP does not meet the minimum requirements is to review the WordPress Dashboard. Your Dashboard can be found at yourdomain.name/wp-admin/. If PHP is out of date, a panel on the left-hand side of the Dashboard displays a “PHP Update Recommended” warning. It cautions that “Your site is running an insecure version of PHP” and encourages you to update it. The panel also displays the minimum recommended version of PHP. This is currently version 7.4. To suppress this warning, PHP must be updated to this version or a more recent one.
How to Check Your Current Version of PHP
There are two ways to find out what version of PHP is currently installed.
Consult the WordPress Dashboard. If PHP is out of date, it displays the current version.
Verify the PHP version of PHP from the command line using the following command.
sudo php -vPHP 7.0.33-52+ubuntu20.04.1+deb.sury.org+1 (cli) (built: Jul 1 2021 16:04:17) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) 1997-2017 The PHP Group
Prepare a Backup in WordPress
Although unlikely, the site or its contents could be corrupted during the update. You should always back up your site before upgrading PHP. There are two parts involved when backing up your site:
- Back up the WordPress site and associated files.
- Back up the WordPress database.
The WordPress site can be backed up externally using FTP or SCP. It can also be backed up in a different folder on the Linode. In the long run, it is much safer to back up the files and database to external storage space. This preserves the archive in the event the server hard drive becomes corrupted or access to the server is permanently lost. However, to quickly upgrade WordPress or PHP, a temporary backup copy can be made somewhere else on the Linode.
To back up the WordPress files on the Linode, follow the below steps:
Create a directory in your home directory to store the WordPress archive.
mkdir wpbackupLocate the
public_htmlfolder containing the WordPress files andcdto this directory. In a standard Apache configuration, this folder is found in/var/www/html/yourdomainname.com.cd /var/www/html/yourdomainname.comCopy the contents of the
public_htmldirectory to thewpbackupdirectory.sudo cp public_html/ -r ~/wpbackupNote To back up files to another system, launch an FTP application from the other system and connect to Linode. Navigate to the/var/www/html/yourdomainname.comand copy over the entire contents of thepublic_htmldirectory. For more information on using FTP, see our Transfer Files with FileZilla guide.
There are several alternatives for backing up a WordPress database. The phpMyAdmin application is a popular choice. Many plug-ins can also back up the database. However, the MySQL utility mysqldump works in all situations without any additional tools. Back up your WordPress database by following the below procedure.
Use the
mysqldumpcommand in the following format,mysqldump -u username --databases database_name > /backup_file.sql.The
usernameis the name of the WordPress MySQL account, but arootaccount can also be used. WordPress prompts for a password if one is required. Thedatabase_nameis the name of the WordPress database. This database was created when WordPress was first installed and is typically namedwordpress. Thebackup_file.sqlvalue indicates the full path of the directory where the backup should be saved.mysqldump -u username wordpress > /backup_file.sql
Update PHP on Ubuntu 20.04
To use a newer version of PHP, all necessary PHP modules must be upgraded to the new version. The current minimum recommended version of PHP is 7.4. To upgrade PHP, follow the instructions below:
Install the basic version of PHP 7.4.
sudo apt install php7.4Note If thephp7.4component cannot be found on the system, version 7.4 might still be the default version. To determine the default version of thephppackage, run the commandsudo apt list php. If this displays a reference to version 7.4, run the commandsudo apt install php. To install a different version of PHP, follow the instructions in the How to Install a Specific Version of PHP section.Install the 7.4 version of the other PHP modules, along with the
libapache2-mod-php7.4component. The following list includes the essential PHP libraries for WordPress.sudo apt install php7.4-common php7.4-mysql php7.4-cgi libapache2-mod-php7.4 php7.4-mbstring php7.4-curl php7.4-gd php7.4-xml php7.4-xmlrpcNote If NGINX is used as the web server, thephp7.4-fpmpackage must also be installed.The
php-pearmodule is also recommended with PHP 7.4.sudo apt install php-pearVerify PHP has been upgraded to version 7.4.
php -vPHP 7.4.21 (cli) (built: Jul 1 2021 16:09:41) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) The PHP GroupDisable the older version of the
libapache2module and enable the new one. The following command illustrates how to disable PHP 7.0 and enable version 7.4.sudo a2dismod php7.0 sudo a2enmod php7.4Note If NGINX is used as the web server, run the following commands instead:
sudo systemctl start php7.4-fpm sudo systemctl enable php7.4-fpmAlso, change the
fastcgi_passvalue in/etc/nginx/conf.d/yourdomain.com.conftofastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;.Consult the Linode guide on NGINX and PHP for more details.
Restart the Apache server to apply the changes.
sudo systemctl restart apache2Reload the WordPress Control Panel. The notification about the outdated PHP application should no longer be visible.
How to Install a Specific Version of PHP
There could be occasions when a different version of PHP is required, for example, when compatibility with a theme must be maintained. To install a specific version of PHP, follow the instructions below.
Depending on the system, the necessary PHP packages might already be available. To determine whether this is the case, follow the steps in the following section.
To verify whether the package for PHP version x.y is already available, run the command
sudo apt list phpx.y. If the command displays details about the package, then it can be immediately installed. Packages are available for all currently supported versions.sudo apt list php7.3Listing... Done php7.3/focal 7.3.29-1+ubuntu20.04.1+deb.sury.org+1 allInstall this version of PHP.
sudo apt install php7.3Update all other PHP packages to the same version at the same time. For example,
php7.3-mysqlandlibapache2-mod-php7.3must also be installed. See the Update PHP on Ubuntu 20.04 section for a complete list.
If the package is not available, it might be available via the ondrej Personal Package Archive (PPA), developed by Ondřej Surý. This archive provides access to the most recent versions of PHP. The same naming convention as above is used.
Add the
ondrej/phprepository usingapt.sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/phpCo-installable PHP versions: PHP 5.6, PHP 7.x and most requested extensions are included. Only Supported Versions of PHP (<http://php.net/supported-versions.php>) for Supported Ubuntu Releases (<https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Releases>) are provided.Add the corresponding
apache2PPA.sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/apache2Upgrade the packages.
sudo apt-get updateInstall the various PHP packages using the instructions in the previous section.
sudo apt install php5.6
If more than one version is installed, set the default version of PHP using the update-alternatives command. The following command sets the default PHP version to 7.0.
sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.0
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/php7.0 to provide /usr/bin/php (php) in manual modeHow to Restore a Backup
The backup procedures are executed in reverse to restore the backup copy.
Before proceeding to restore the backups, inspect the site. If all the content is still available and the site is behaving normally, it might not be necessary to restore the archive. If any content appears to be missing, something does not look right, or to guarantee the site content has not changed, proceed with the next steps.
Copy the backup copy of the WordPress site from the temporary directory to
/var/www/html/yourdomainname.com/public_html.cd ~/wpbackup sudo cp public_html/ -r /var/www/html/yourdomainname.comEnter the MySQL database.
sudo mysql -u rootThe database must be empty before it can be restored, so it must be dropped and then re-created. In most cases, the WordPress database is named
wordpress, but it might have been given another name at installation time. To list all of the MySQL databases, run the commandSHOW DATABASES;.DROP DATABASE wordpress;Re-create the database and grant privileges to the WordPress user. Replace
usernamewith the name of the actual WordPress user account.CREATE DATABASE wordpress; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'username'@'localhost';Exit the MySQL database, and restore the old database using the
mysqlcommand. Do not usemysqldumpbecause this does not accurately re-create the database schema. Replace theusernamefield with the actual name of the WordPress account and specify the path to the location of thesqldatabase archive.mysql -u username -p wordpress < /pathto/filename.sqlLogin back into the WordPress site and verify the content is present and the site behaves as expected. WordPress asks you for the username, password, and database name again. This is because the original
wordpresstable no longer exists and it must re-evaluate your credentials.(Optional) You might want to take this opportunity to upgrade all themes and plug-ins and inspect the WordPress Dashboard for any further issues. It is also a good idea to remove any unused plug-ins.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on
